Creators produce an unprecedented amount of content, from videos and music to blog posts and artwork. While this explosion of creativity offers numerous opportunities, it also presents challenges, particularly in protecting one’s creative work from unauthorized use. Understanding copyright rules is essential for you as a creative, to safeguard your intellectual property and ensure your creative rights are respected.

Image from Investopedia
What Does Copyright Protect?

Image from Broadcast Beat
Copyright protects the expression of ideas, not the ideas themselves. For example, the plot of a story is not copyrightable, but the specific words and arrangement of those words are. Copyright also gives the creator of the work the exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, perform, display, or create derivative works based on the original.
Duration
In most countries, copyright protection lasts for the life of the creator plus an additional 50 to 70 years. However, for works created by corporations or anonymously, the duration typically ranges from 95 to 120 years from publication.
What Constitutes Copyright Infringement?

Image from LinkedIn
Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses copyrighted material without permission from the copyright holder. This includes:
Reproduction: Making copies of the work, such as photocopying a book or downloading a song.
Distribution: Copying and distributing the work to others, such as selling pirated copies.
Public performance: Performing the work publicly, such as showing a movie without a license.
Public display: Displaying the work publicly, such as showing a painting in a gallery without permission.
Creation of derivative works: Creating new works based on the original, such as making a movie based on a book.
Fair Use: An Exception to Copyright
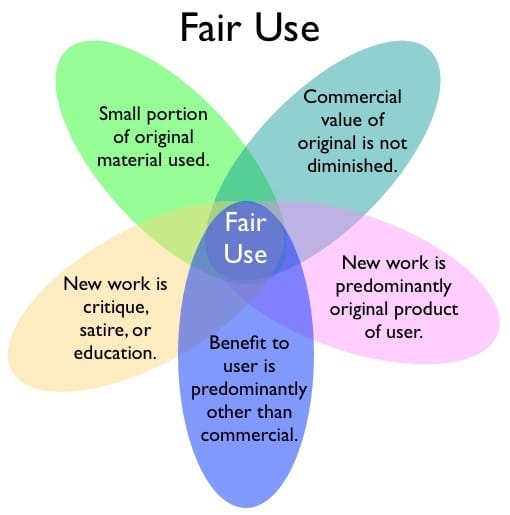
Image from Linked In
Fair use is a legal doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holder. Factors considered in determining fair use include:
Purpose and character of the use: Is the use commercial or non-profit educational?
Nature of the copyrighted work: Is the work factual or creative?
Amount and substantiality of the portion used: How much of the original work is used?
Effect of the use on the potential market for or value of the copyrighted work: Does the use harm the market for the original work?
Protecting Your Creative Work
To protect your creative work, consider the following steps:
Register your copyright: While not required, registering your copyright with the appropriate copyright office provides additional legal protections.
Use copyright notices: Indicate that your work is copyrighted by using the copyright symbol ©, your name, and the year of creation.
Keep records of your work: Keep records of when you created your work and any evidence of its originality.
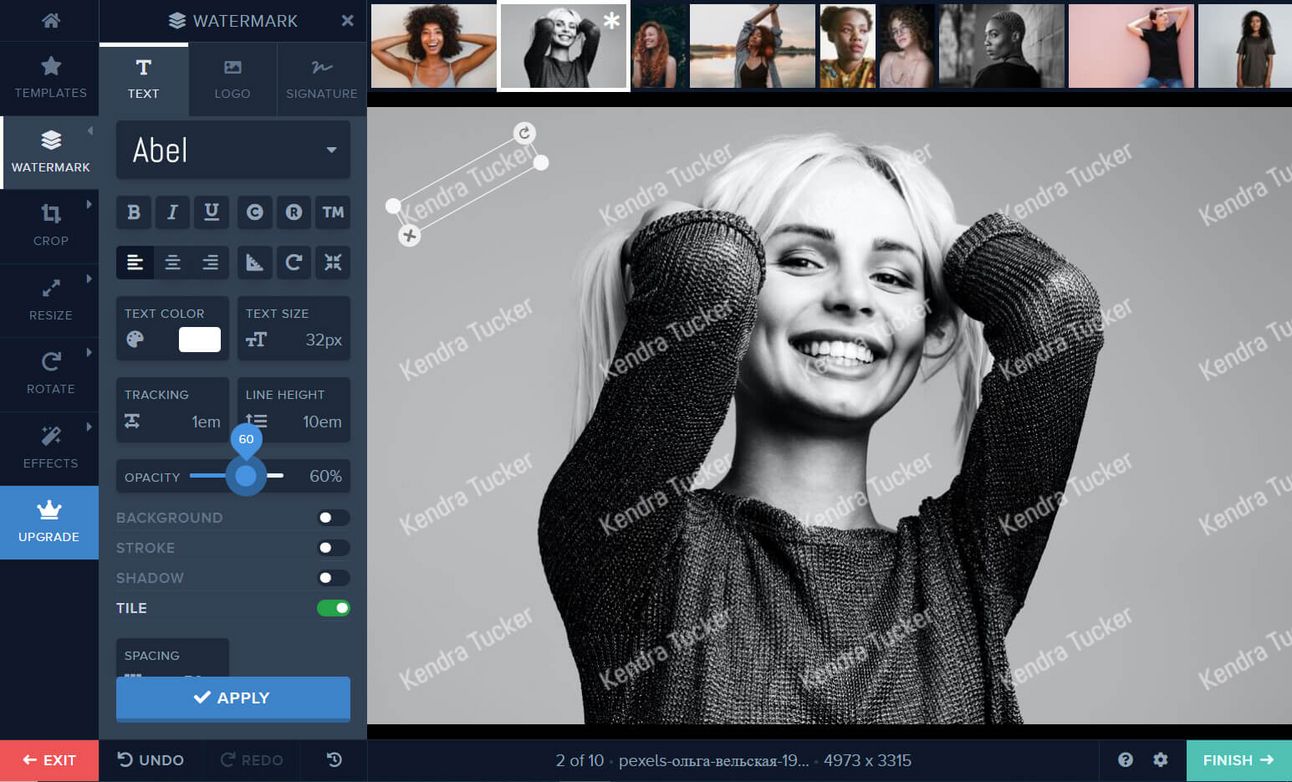
Use copyright management systems: You can also consider using digital watermarking or other technologies to protect your work.
Copyright is a vital tool for protecting the rights of creators in this fast-paced age. Understanding copyright rules and fair use means creators can better safeguard their work and ensure it is used in a manner that respects their rights.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and does not constitute legal advice. It is recommended to consult with an attorney for advice regarding specific copyright matters.
